Again in the list of "BPM Blogs worth reading 2012" from Alberto Manuel.
See http://ultrabpm.wordpress.com/2012/12/12/bpm-blogs-worth-reading-2012/
Thanks,
AS
2012-12-12
2012-11-27
An example of #entarch contributing to a business strategy
"The aim of this Brief is to outline how the coherent use of several existing information technologies can significantly accelerate the achievement of the vision stated in the Bank’s Long-Term Strategy (LTS)."
UNIQUE OPPORTUNITY FOR AFRICA: ARCHITECTING THE SYNERGY BETWEEN EXISTING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES
Thanks,
AS
UNIQUE OPPORTUNITY FOR AFRICA: ARCHITECTING THE SYNERGY BETWEEN EXISTING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES
Thanks,
AS
2012-11-17
SAP Tech 2012 Madrid 4th half-day
4 hours hands-on workshop for SAP PI 7.31 (PMC262):
1) good complimentary work between BPMs and PI
2) majority of PI configuration from Eclipse
3) simple configuration of PI's information flows
4) naming convention from SAP (!)
5) boundary between BPMs and PI is flexible thus requires good recommendations. For example, PMC262 puts some logic in PI while I would consider to put the same logic in BPM (actually in its inter-process communication part) for easier maintenance and monitoring. In case of performance, it may go to PI.
6) configurable alerts
Thanks,
AS
1) good complimentary work between BPMs and PI
2) majority of PI configuration from Eclipse
3) simple configuration of PI's information flows
4) naming convention from SAP (!)
5) boundary between BPMs and PI is flexible thus requires good recommendations. For example, PMC262 puts some logic in PI while I would consider to put the same logic in BPM (actually in its inter-process communication part) for easier maintenance and monitoring. In case of performance, it may go to PI.
6) configurable alerts
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
SAP,
SAPTech2012
2012-11-15
SAP Tech 2012 Madrid 3rd day
1) Agile implementation methodology ASAP 8: SCRUM-based + accelerators(!)
2) Accelerators example: irise for mock-up; co-development and co-innovation
3) Roles management in NW identity management
4) Visual composer and adobe forms are dead - use HTML5 kit
5) BW may be on top of Hana
6) NW gateway for human-centric applications; potential emdebbing into NW
7) SAP is moving to the core banking and Africa
8) NW PI is a normal ESB
9) NW in the cloud: ability to work together with SAP's dev teams!
Thanks,
AS
2) Accelerators example: irise for mock-up; co-development and co-innovation
3) Roles management in NW identity management
4) Visual composer and adobe forms are dead - use HTML5 kit
5) BW may be on top of Hana
6) NW gateway for human-centric applications; potential emdebbing into NW
7) SAP is moving to the core banking and Africa
8) NW PI is a normal ESB
9) NW in the cloud: ability to work together with SAP's dev teams!
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
SAP,
SAPTech2012
2012-11-14
SAP Tech 2012 Madrid 2nd day
1) NetWeaver BPM can handle many pools in one diagram - pools are treated as separate processes (templates and processes) in case of async invocation
2) Event layer is available to externalise events from SAP ECC6, NW and SAP WF - this is a way to understand existing implicit processes
3) CEP engine is coming
4) It seems that BW will be replaced by something based on HANA
5) HTML5 is the choice to go to mobile apps which should work on-line and off-line
6) SUP is the way to communicate between SAP and mobile
+ A very good ipad application as a conference guide with personalised agenda
Thanks,
AS
2) Event layer is available to externalise events from SAP ECC6, NW and SAP WF - this is a way to understand existing implicit processes
3) CEP engine is coming
4) It seems that BW will be replaced by something based on HANA
5) HTML5 is the choice to go to mobile apps which should work on-line and off-line
6) SUP is the way to communicate between SAP and mobile
+ A very good ipad application as a conference guide with personalised agenda
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
SAP,
SAPTech2012
2012-11-13
SAP Tech 2012 Madrid 1st day
A few quick points:
1) Synergetic mobile+cloud+big data offer
2) Fun with NetWeaver development studio exercise which looks similar to Intalio thus easy to complete the job first in the class :)
3) Impressively strong internal EA function at SAP AG
Thanks,
AS
1) Synergetic mobile+cloud+big data offer
2) Fun with NetWeaver development studio exercise which looks similar to Intalio thus easy to complete the job first in the class :)
3) Impressively strong internal EA function at SAP AG
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
SAP,
SAPTech2012
2012-09-22
Practical process anti-pattern: NAP
No Aggregated Participant (NAP)
It was noticed that the use of swimlines forces to put too much details in the diagram thus making it not easy to understand. With swimlines there is no place for a group of "tiny" activities which are carried out by several participants (each of them already has her/her own swimline), or "aggregated participant".
Without swimlines the use of "aggregated participant" may simplify complex diagrams.
This simplified diagram is very close the pattern IPS (Initial Process Skeleton, see my book www.samarin.biz/book) and the "Approve proposal" activity is similar to the pattern DAM (Delegation Authority Matrix - see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/practical-process-pattern-dam.html).
Actually, we follow the pattern DIP (Decompose In Patterns - see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/06/practical-process-patterns-dip.html ).
Thanks,
AS
It was noticed that the use of swimlines forces to put too much details in the diagram thus making it not easy to understand. With swimlines there is no place for a group of "tiny" activities which are carried out by several participants (each of them already has her/her own swimline), or "aggregated participant".
Without swimlines the use of "aggregated participant" may simplify complex diagrams.
This simplified diagram is very close the pattern IPS (Initial Process Skeleton, see my book www.samarin.biz/book) and the "Approve proposal" activity is similar to the pattern DAM (Delegation Authority Matrix - see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/practical-process-pattern-dam.html).
Actually, we follow the pattern DIP (Decompose In Patterns - see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/06/practical-process-patterns-dip.html ).
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
#ACM,
#BPM,
BPM,
practical process patterns
Practical process anti-pattern: RID
The anti-pattern Ruined in Details (RID) was detected while looking at business processes documented by the users. Often, the sequence of activities (or tasks) is the following:
...
Role B: receive documents from role A
Role B: do your work
Role B: send documents to role C
Role C: receive documents from role B
Role C: do your work
Role C: send documents to role D
...
Sure that receiving and sending documents are important, but those activities don't add the value. Indicating only value-added-value activities (e.g. "do your work") will make diagrams more compact and easier to understand.
Maybe this anti-pattern is a sign that there are problems with integration?
Thanks,
AS
...
Role B: receive documents from role A
Role B: do your work
Role B: send documents to role C
Role C: receive documents from role B
Role C: do your work
Role C: send documents to role D
...
Sure that receiving and sending documents are important, but those activities don't add the value. Indicating only value-added-value activities (e.g. "do your work") will make diagrams more compact and easier to understand.
Maybe this anti-pattern is a sign that there are problems with integration?
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
#ACM,
#BPM,
BPM,
practical process patterns
2012-09-02
Re: BPM vs. BPMS: How To Think Big and Act Small
This is a reply to http://isismjpucher.wordpress.com/2012/08/27/bpm-vs-bpms-how-to-think-big-and-act-small/ blogpost.
Thanks Max for a good post which is commented below from my "managing by business processes (BPM) methodology" (www.samarin.biz/book and http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/).
I disagree with you that BPM == "flow-charting". Certainly, BPM may use several coordination techniques – see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/coordination-techniques-in-bpm-social.html
Also, I disagree with you that "adaptive processes" are not possible in BPM – see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2010/12/illustrations-for-bpm-acm-case.html
I agree with you that BPM as discipline and BPMS are very different things. In my experience, they can be perfectly used within a proper architecture (i.e. “to think big”).
My experience relative “The NINE Contradictions in BPM Implementation Principles” (BTW, what is the origin of those principles?) is below.
Obviously there are several different BPMS, few BPM methodologies, a huge number of BPM implementations, but still missing parts are BPM reference model and BPM reference architectures.
Thanks,
AS
Thanks Max for a good post which is commented below from my "managing by business processes (BPM) methodology" (www.samarin.biz/book and http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/).
I disagree with you that BPM == "flow-charting". Certainly, BPM may use several coordination techniques – see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/coordination-techniques-in-bpm-social.html
Also, I disagree with you that "adaptive processes" are not possible in BPM – see http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2010/12/illustrations-for-bpm-acm-case.html
I agree with you that BPM as discipline and BPMS are very different things. In my experience, they can be perfectly used within a proper architecture (i.e. “to think big”).
My experience relative “The NINE Contradictions in BPM Implementation Principles” (BTW, what is the origin of those principles?) is below.
- If BPM would be capable of being business-driven then there is no need for executive enforcement.
AS: It is possible to be business-driven if BPM is properly architected. - If the implementation of processes would really happen through users there is no need for governance.
AS: It is for business to decide. Some governance is always necessary, maybe business one not IT one. - As business users can maybe draw a flow-diagram but can’t make it executable, the BPM stages are all performed by experts, actually reducing agility.
AS: Not necessary “reducing”, as the IT agility maybe higher (thanks to the architecture) than the business agility. - Both BPM methodology and BPMS ignore that users understand processes in terms of content and context and not in flow-diagrams.
AS: Not at all. Processes are positioned as the help for the users to carry out their work including also the handling the content. - To change business culture is a long term prospect and collides with short ROI time frames.
AS: BPM applications are the best example of agile projects. The ROI is great. - What kind of culture change should be necessary to motivate people to follow flow-diagrams all day.
AS: Again, disagree that BPM == “flow-diagrams” - To reduce scope creep and ensure ROI, governance limits end-user requirements and achievable quality.
AS: IT governance or business governance? In any case, late changes of user’s requirements are very welcome. - A holistic BPM methodology is then fragmented over many different software products for implementation.
AS: Yes, BPM is vendor-driven so far. - As the fragmentation requires governance, any change requires long-term planning and therefore reduces actual business agility.
AS: The architecture enables the agility. - If a BPMS is chosen to match current needs and maturity level then it has to be replaced frequently as the business matures.
AS: The architecture also helps with this.
Obviously there are several different BPMS, few BPM methodologies, a huge number of BPM implementations, but still missing parts are BPM reference model and BPM reference architectures.
Thanks,
AS
Practical process anti-pattern: DOUM
Avoid the "DOUble Master" (DOUM) anti-pattern (section 5.6 of my book "Improving enterprise BPM systems")
As coordination can be carried out by an application or by a process engine, we have to be very careful to avoid the “double master” anti-pattern. At any moment in time there must be only one master responsible for the coordination of a particular process instance. (Of course, the coordination role may be delegated if appropriate.) This is analogous to a well-organised meeting where the chairperson decides who talks next.
Also well-coordinated work improves the security and integrity of data. It can be a useful design pattern to consider that only the person who has accepted a particular human activity can modify the business objects associated with that human activity. This is a dynamic granting/revoking of permissions which is synchronised with the process. Something like in the diagram below (which is not a valid BPMN as there are no "claim" and "unclaim" events defined).
The non-recognition of this anti-pattern can be very costly. We have observed a BPM solution which allowed the modification of data by a process engine, by an interactive application (i.e. by a human) and by a batch at the same time. The coordination of activities was based on data and, if necessary, the application or the batch could “correct” the process. The process engine was used mainly for the handling of three human activities, and the implementation of this solution (for a relatively simple business process) took several man-years.
Thanks,
AS
As coordination can be carried out by an application or by a process engine, we have to be very careful to avoid the “double master” anti-pattern. At any moment in time there must be only one master responsible for the coordination of a particular process instance. (Of course, the coordination role may be delegated if appropriate.) This is analogous to a well-organised meeting where the chairperson decides who talks next.
Also well-coordinated work improves the security and integrity of data. It can be a useful design pattern to consider that only the person who has accepted a particular human activity can modify the business objects associated with that human activity. This is a dynamic granting/revoking of permissions which is synchronised with the process. Something like in the diagram below (which is not a valid BPMN as there are no "claim" and "unclaim" events defined).
The non-recognition of this anti-pattern can be very costly. We have observed a BPM solution which allowed the modification of data by a process engine, by an interactive application (i.e. by a human) and by a batch at the same time. The coordination of activities was based on data and, if necessary, the application or the batch could “correct” the process. The process engine was used mainly for the handling of three human activities, and the implementation of this solution (for a relatively simple business process) took several man-years.
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
#security,
practical process patterns
2012-07-29
Practical process pattern: DAM
Delegation of Authotirty Matrix (DAM) is a popular corporate tool which specifies what role is authorized for what functions in particular case. For example, a Director can approve purchasing of some services for less than 50’000 USD; more costly services must be approved by a Vice-President. Of course, the corporate approval logic must be a unique service and not “implemented” by a few gateways in each process.
The following diagram shows a possible usage of DAM.
Thanks,
AS
The following diagram shows a possible usage of DAM.
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
practical process patterns
Practical process pattern: SAAP
Servicing As A Process (SAAP) pattern was observed in “implied” business processes (http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/practical-process-pattern-mimo.html). It is implied that an organisation-unit-oriented (or functional) process is invoked from a bigger (almost end-to-end) process. Actually, the former is invoked to serve client’s requests and servicing of different request may overlap in time. Thus, each service invocation should be a separate instance (see the diagram below).
So, there are elements of a mass service system – an input flow of requests for service has to be served in accordance with a potential SLA and by a limited number of servicing slots. (Like a barber shop.)
In the diagram above, the several coordination techniques (http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/coordination-techniques-in-bpm-social.html) were used, namely: template-based, event-based, instance-based, and information-based (to manage the number of available slots – in an implicit way).
Thanks,
AS
So, there are elements of a mass service system – an input flow of requests for service has to be served in accordance with a potential SLA and by a limited number of servicing slots. (Like a barber shop.)
In the diagram above, the several coordination techniques (http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2012/07/coordination-techniques-in-bpm-social.html) were used, namely: template-based, event-based, instance-based, and information-based (to manage the number of available slots – in an implicit way).
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
practical process patterns
2012-07-15
Practical process pattern: MIMO
Pattern Multiple Instances Multiple Objects (MIMO) is observed in some business process diagrams provided by the business as documentation for their business processes. I call such business processes “implied”.
Typical case is the institutional (corporate) procurement process which is described as the following:
It looks very straightforward. But a PR may contain many positions which can be sourced by different methods:
And each of those methods requires its own process. So, multiple objects in the instance of “Submit PR” process may initiate multiple instances of sourcing processes (see the diagram below). This effect of is implied in the user’s documentation.
Events, generated by the “Submit PR” process, can be treated as describe in http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/01/explicit-event-processing-agents-in.html
Thanks,
AS
- Submit Purchase Requisition (PR)
- Choose Supplier
- Issue Purchase Order (PO)
- Receive Goods / Services
- Pay Invoice
It looks very straightforward. But a PR may contain many positions which can be sourced by different methods:
- From the stock
- From a known (preferred) supplier
- From an unknown (via a bid) supplier
And each of those methods requires its own process. So, multiple objects in the instance of “Submit PR” process may initiate multiple instances of sourcing processes (see the diagram below). This effect of is implied in the user’s documentation.
Events, generated by the “Submit PR” process, can be treated as describe in http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/01/explicit-event-processing-agents-in.html
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
practical process patterns
2012-07-08
Quick delivery of solutions via a PEAS-architected platform
The aim of this post is to outline how to organise the quick delivery of solutions via a platform architected in accordance with the PEAS enterprise pattern.
Mini-projects are carried-out by solution architects (business analysts, technical staff, super-users from the business units, etc. - depending on their complexity).
Platform implementation resources (programmers and configurators) are provided by the IT department and by a set of authorised service providers (platform vendor and its authorised partners).
Operational team provides integration and release of solutions into production.
AS
The business need
Users’ demands are typically numerous, have many overlapping features and will be implemented with different pace (because different users’ units work with different speed). The challenge is to achieve the synergy between different demands and capabilities of the platform. It can be addressed by a proper combination of architecture (PEAS enterprise pattern), governance structure and implementation practices.Decomposition into several basic functionalities
Vast majority of users’ demands correspond to several basic functionalities or combinations of them. For example, in an ECM-platform such typical functionalities are:- Information site
- Collaboration site
- Workflow
- Data collection
- Common storage
- Business manual (a la wiki)
- Public site
- Extranet site
- Integration with Outlook
- Securing documents
- Access from iPad
- Integration with archive
- Integration with SAP
Readiness review
Potential projects are in rows and functionalities are in columns. Each project requires some functionalities for its 1st and 2nd parts (phases). Each functionality is at the different level of readiness: green, yellow and red. This allows estimating the readiness for 1st and 2nd parts of each project. The popularity of each functionality can be estimated also.Governance structure
There are two primary types of activities:- On-going and centralised platform governance: evolution of architecture, evolution of features, evolution of solutions, evolution of practices.
- Rapid implementation of solution as a mini-project – light specifications, quick prototyping, consistent configuration, fast procurement, agile development, and re-use of existing tools and habits.
Mini-projects are carried-out by solution architects (business analysts, technical staff, super-users from the business units, etc. - depending on their complexity).
Platform implementation resources (programmers and configurators) are provided by the IT department and by a set of authorised service providers (platform vendor and its authorised partners).
Operational team provides integration and release of solutions into production.
Implementation practices
Implementation practices should be as light as possible without any internal barriers. In any case, we will work with the speed of the users.- Users’ demand is understood by the business analyst (BIZAN).
- If the BIZAN finds that this demand is too complex then it is escalated to the PLACOCO to assign another solution architect (SA) otherwise the BIZAN acts as the SA.
- The solution dossier is prepared by the SA with the help of other staff members. A prototype is prepared if necessary.
- If the solution dossier shows that a proposed solution is NOT straightforward (a set of rules to be defined and it can evolve over the time) then the PLACOCO evaluates it and approves any new features/extensions (if necessary).
- The solution dossier is transferred to the internal pool of platform implementation resources to come up with the resource allocation.
- If internal resources are not adequate (too busy or/and lack of expertise) then the solutions dossier is escalated to the external pool of platform implementation resources.
- Mini-project team (including super-users) is formed and it iterates with the users to finalise the solution.
- Solution is operationalized following the change management process.
AS
Labels:
#platform,
agility,
enterprise patterns,
PEAS
2012-07-07
Coordination techniques in BPM, Social, ACM, etc.
Considering the definition of a process as “explicitly-defined coordination of services to create a particular result” this post shows how some explicit coordination techniques (rows) are employed by different “methodologies” (columns) for managing the business by processes.
A combination of some of them may provide "predictive analytics".
Ideally – like in the chess game – use must the right combination of coordination techniques in a particular case at the particular moment. But, not all process-centric tools offers all coordination techniques.
Also a related post about BPM and ACM - http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2010/12/illustrations-for-bpm-acm-case.html.
Thanks,
AS
Classic WF
|
Classic BPM
|
ACM
|
Social NNN
|
EPN
|
|
template-based
|
++
|
++
|
--
|
--
|
-+
|
event-based
|
-+
|
+-
|
+-
|
-+
|
++
|
rule-based
|
++
|
++
|
+-
|
-+
|
+-
|
role-based
|
++
|
++
|
+-
|
-+
|
-+
|
information-based
|
-+
|
-+
|
+-
|
+-
|
-+
|
intelligence-based
|
-+
|
-+
|
-+
|
+-
|
--
|
community-based
|
--
|
--
|
-+
|
++
|
--
|
goal-based
|
--
|
--
|
+-
|
-+
|
--
|
instance-based
|
--
|
-+
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
interprocess (used instance-based)
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
managerial (tacit-knowledge-based)
|
--
|
-+
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
resource-based (follow the resource life-cycle)
|
--
|
-+
|
+-
|
--
|
--
|
inter-organisation
|
--
|
-+
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
state-based ??
|
??
|
??
|
??
|
??
|
??
|
A combination of some of them may provide "predictive analytics".
Ideally – like in the chess game – use must the right combination of coordination techniques in a particular case at the particular moment. But, not all process-centric tools offers all coordination techniques.
Also a related post about BPM and ACM - http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2010/12/illustrations-for-bpm-acm-case.html.
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
#ACM,
#best,
#BPM,
#egov,
#entarch,
ACM,
BPM,
case management,
coordination,
e-government,
EPN,
SAP,
workflow
2012-06-27
Writing IT strategy - From business priorities to the planning of IT actions
This post is the continuation of the post "Writing IT strategy" - http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/09/writing-it-strategy.html
The explicit dependencies between business-specific initiatives, business-generic needs (or business capabilities), IT-generic capabilities and programs demonstrated in figure below allow to explicitly linking the business priorities with the planning of IT actions. The logic of linking is the following:
The explicit dependencies between business-specific initiatives, business-generic needs (or business capabilities), IT-generic capabilities and programs demonstrated in figure below allow to explicitly linking the business priorities with the planning of IT actions. The logic of linking is the following:
- each business-specific initiative has its own corporate priority;
- each business-specific initiative requires a particular level of maturity of some existing business-generic needs;
- each business-generic need has its own current level of maturity (can be determined by experts) and the requested level of maturity (so a gap can be identified);
- particular level of maturity for each business-generic need depends on a particular level of maturity of some existing IT capabilities;
- each IT capability has its own current level of maturity (can be determined by experts) and requested level of maturity (so a gap can be identified);
- programmes to close gaps are proposed, and
- priorities of programmes are defined by the contribution into business priorities.
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
EA,
IT strategy
2012-04-09
Architecting modern information systems
My course "Architecting modern information systems" (please, see its structure below) is available at slideshare.net.
The class in Tunisia:
Module 1: Enterprise architecture (EA) http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-of-modern-information-systems-m1
Module 2: Business architecture http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m2a and http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m2a-business-architecture
Module 3: Application architecture http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m2b-application-architecture
Module 4: Information architecture http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m4-information-architecture
Module 5: Technology architecture
Module 6: Modern disruptive technologies http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m6-modern-disruptive-technologies
Module 7: Essential techniques http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m7-essential-techniques
AS
Lettre de remerciement
The class in Tunisia:
Module 1: Enterprise architecture (EA) http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-of-modern-information-systems-m1
- Architecture within an enterprise
Module 2: Business architecture http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m2a and http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m2a-business-architecture
- Management by processes
Module 3: Application architecture http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m2b-application-architecture
- Link applications to the business
- Technologies: BPM, BRM, BEM, BAM
- SOA, Integration (ESB), Application systems (suites)
Module 4: Information architecture http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m4-information-architecture
- Knowledge management
- Technologies: ECM, MDM, BI, risk management
Module 5: Technology architecture
- Flexibility systems
- Security considerations
- Virtualisation
Module 6: Modern disruptive technologies http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m6-modern-disruptive-technologies
- Cloud computing
- Social computing
- Free and Open Source Software; Open standards
Module 7: Essential techniques http://www.slideshare.net/samarin/architecting-modern-informaiton-systems-m7-essential-techniques
- Project management (PMBOK, HERMES)
- Governance (COBIT)
- Writing the IT strategy
AS
Lettre de remerciement
Labels:
africa
2012-01-14
Enterprise pattern: SITO, extended
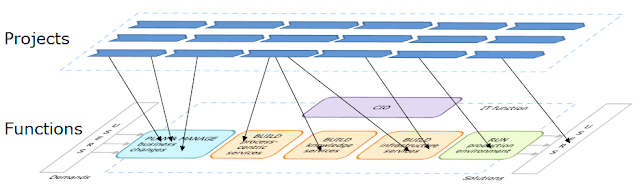
Comments to SITO enterprise pattern (see the updated version of it at http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/10/enterprise-pattern-structuring-it.html ) were that it is too classic. Sure, structuring is the first step to establish the balance between functions and projects.
Next step is how to preserve, enrich and re-use the technical/business knowledge and experience gained in each project. A possible way is to create competence forums which are oriented to deliver business-generic services (or "needs" as they mentioned in http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/09/writing-it-strategy.html ). Usually, such services are based on several IT-generic services which are mastered in different IT functions.
How those competence forums to be managed to avoid over complication and conflicts of responsibilities? Competence forum is led by the CIO with the help from an informal leader from the participants. For example, the CIO chaired a few initial meetings and then delegates the routine work to the informal leader.
Next step, the IT governance, was already covered in http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/01/relationships-between-ea-and-pmo.html . Just a small addition to that post:
Thanks,
AS
Next step is how to preserve, enrich and re-use the technical/business knowledge and experience gained in each project. A possible way is to create competence forums which are oriented to deliver business-generic services (or "needs" as they mentioned in http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/09/writing-it-strategy.html ). Usually, such services are based on several IT-generic services which are mastered in different IT functions.
How those competence forums to be managed to avoid over complication and conflicts of responsibilities? Competence forum is led by the CIO with the help from an informal leader from the participants. For example, the CIO chaired a few initial meetings and then delegates the routine work to the informal leader.
Next step, the IT governance, was already covered in http://improving-bpm-systems.blogspot.com/2011/01/relationships-between-ea-and-pmo.html . Just a small addition to that post:
- EA (or EITA) defines/monitors WHAT should be done (technical coordination of the enterprise IT environment).
- PMO defines/monitors HOW it should be done (administrative coordination of changes in the enterprise IT environment).
Thanks,
AS
Labels:
#entarch,
EA,
enterprise architecture,
enterprise patterns,
ITIL,
PMO,
SAP
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)